How Do You Treat Diabetes? Medications, Diet, Stem Cells

It’s possible for you to treat diabetes. Diabetes is a serious disease with many long-term health consequences. While there is currently no cure, there are different ways to treat diabetes so it remains under control and you can live a full life. Learn ways to do that below.
As you treat and manage your diabetes, you won’t be alone. You’ll work with a treatment team consisting of multiple health care professionals that may include:
- Your primary care physician
- Diabetes educator
- Endocrinologist
- Ophthalmologist or optometrist
- Podiatrist
- Dentist
- Exercise physiologist
- Nutritionist
- Mental health therapist
Perhaps the most important person on your diabetes treatment team is you. When you take an active roll in your health and diabetes management, you will be more successful in leading a healthy life.
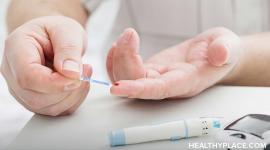
How Do You Treat Diabetes? Blood Glucose Monitoring
Diabetes is high blood glucose (blood sugar), or hyperglycemia. In diabetes, there is a problem with the hormone insulin that prevents glucose from entering the body’s cells. It thus accumulates in the bloodstream and your blood sugar levels become too high, leading to a host of health problems.
The first step in controlling your blood glucose levels is to know what they are so you can take measures to get them into the healthy range. You want your glucose to be 70-130 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) before meals and lower than 180 mg/dL after meals. Knowing your numbers guides the actions you take as part of diabetes treatment.
Diabetes Treatment Medications
Diabetes is frequently treated with medication. Depending on the type and how it is affecting you, you may be prescribed insulin or other diabetes treatment medications ("Complete List of Diabetes Medications for Type 1 and Type 2").
Diabetes treatment with insulin is required in type 1 diabetes because the body doesn’t produce its own insulin. Insulin is sometimes used in type 2 diabetes treatment.
Diabetes treatment medications, including insulin, won’t be effective if used alone. Lifestyle is as important as medication for long-term management success.
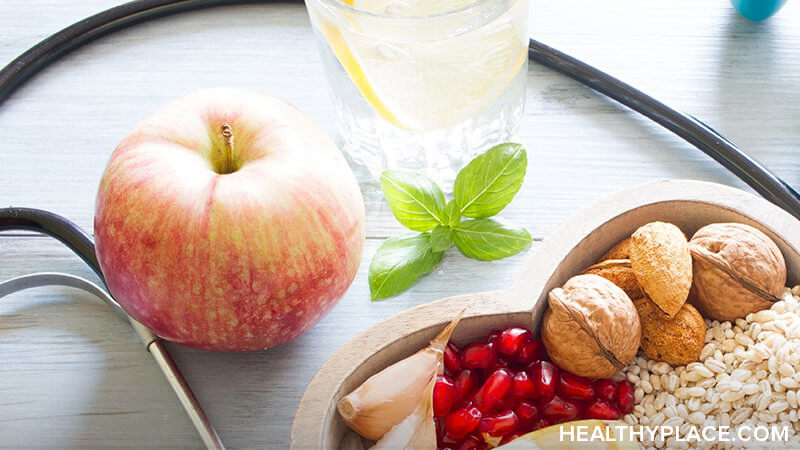
Diabetes Treatment: Diet and Exercise
Everything you eat, both quality and quantity, has an impact on diabetes. The right diet lowers blood sugar and contributes to weight loss. (Obesity is a risk factor in type 2 diabetes.)
A helpful tool for people with diabetes is the glycemic index, a scale—numbering from one to 100—that rates how a specific food affects blood sugar. The lower the number, the less a food increases blood sugar. Foods below 55 on the glycemic index are best in a diabetes treatment diet. Examples of such foods:
- Most fruits
- Vegetables
- Beans
- Minimally refined pasta and grains
- Nuts
- Low-fat dairy products
Additionally, a diet high in protein and fiber helps keep blood sugar under control.
Physical activity is an essential component of diabetes treatment. A sedentary lifestyle is unhealthy in many ways, including how it impacts blood glucose levels. Even mild exercise and movement every day helps reduce hyperglycemia.
Blood glucose monitoring, medications and insulin, and lifestyle components will always be necessary. There’s hope on the horizon for a new treatment that could be a diabetes treatment game-changer.
Diabetes Treatment: The Promise of Stem Cells
Researchers are going to the source of the problem: insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas that either don’t produce insulin (type 1) or don’t produce enough (occasionally in type 2). What if the body could regain the ability to make beta cells and thus insulin?
Diabetes treatment with stem cells could be the answer. Stem cells, found in embryonic tissue, some adult tissue, or made in the lab, can transform into any type of cell. Research continues to determine how to make stem cells get to the pancreas, turn into beta cells, survive as beta cells, and begin making insulin. In time, diabetes treatment with stem cells could provide consistent relief and improvement for those with this disease.
Diabetes Treatment: Unpredictable but Possible
Jordan Morris is a professional soccer player who was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at age nine ("What Are the Symptoms of Diabetes in a Child?"). Determined not to let the disease limit his life, he actively treated it, persevered, and has realized his dream of playing soccer professionally. He is thriving, but still, he admits,
“Even now, [diabetes] is still tough for me to deal with at times because it’s so unpredictable. You can eat the same food, do the same workout on two different days and your blood sugar will turn out differently.” —Jordan Morris, Jordan Morris Foundation for children with type 1 diabetes
He is proof that diabetes treatment is possible and allows you to live fully and accomplish your dreams. He also captures the difficulty of diabetes treatment and why daily blood glucose monitoring, using prescribed medications, including insulin, and daily self-care are vital ("Are There Natural Diabetes Treatments?"). Take an active role in your diabetes treatment to thrive in your life.
APA Reference
Peterson, T.
(2022, January 4). How Do You Treat Diabetes? Medications, Diet, Stem Cells, HealthyPlace. Retrieved
on 2025, May 31 from https://www.healthyplace.com/diabetes/treatments/how-do-you-treat-diabetes-medications-diet-stem-cells